
Math 445 Midterm Test
Problem 1
Suppose a spherical triangle ABC has angle = 80 degrees at each vertex. If the surface area of the sphere is S, what is the spherical area of this triangle?
Problem 2
(a) Find the point C on line AB so that AC/CB = -3/7, where A = (1, 1, 1), B = (0, 2, 3). It is OK to leave your work "unsimplified" or "factored" so long as it is numeric.
C = (7/4)A + (-3/4)B = (7/4, 1/4, -1/2)
(b) At what point D does line AB intersect the (x,y, 0) plane?
D = (3/2)A +(-1/2)B =(3/2, 1/2, 0).
Method: D = (1-t)A + tB. We want to solve for t so that z = 0 for D. The z-coordinate of D is 1(1-t) + 3t = 1 + 2t = 0 when t = -1/2.
Then D = (3/2)A +(-1/2)B = (3/2)(1, 1, 1) +(-1/2)(0, 2, 3) = (3/2, 1/2, 0).
Problem 3
Suppose one makes a cylinder by cutting out the strip between the two parallel lines and taping the edges together. Suppose that you draw two segments of straight paths (i.e., "lines" or geodesics) on the cylinder from A to B. Then you cut the tape and flatten the strip again.
· Draw below what you would see of the two segments. You should show the work that you did to make the drawing accurate, but the drawing does not have to be a straightedge and compass construction. (Of course there is more than one correct answer here.)
Answer: One segment is just the Euclidean segment from A to B. A second segment must go out one edge and back another (one or more times). But this is not just a sketch. The exact location where the segment crosses the edge must be constructed. The way to construct such a segment from A to the upper edge, for example, would be to translate B by the translation T perpendicular to the edges that takes the lower edge to the upper edge. This will translate B to a point B' above the upper edge. Draw the line segment from A to B'. This segment will cross the edge at a point C. Then construct the point D on the lower edge so that CD is perpendicular to the edges. Then the segment DB is the rest of the cylindrical segment. There are an infinite number of line segments on the cylinder from A to B, but they all involve connecting A to a translation of B by T or a power of T.

Problem 4: Barycentric Coordinates
(a) This lattice of points in this figure is made of parallelograms, as it appears. Find the indicated barycentric coordinates and write the answers in the table below. Most answers are by inspection, but a couple will require computation.
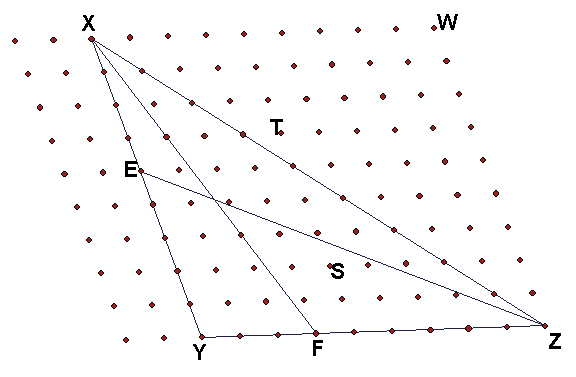
|
Point |
Barycentric Coordinates with respect to triangle XYZ |
|
E |
(5/9, 4/9, 0)
|
|
F |
(0, 6/9, 3/9) = (0, 2/3, 1/3)
|
|
S |
(2/9, 3/9, 4/9)
|
|
T |
(6/9, -1/9, 4/9)
|
|
W |
(9/9, -9/9, 9/9) = (1, -1, 1)
|
|
P = the intersection of lines XF and ZE |
(5/11, 4/11, 2/11) - see below
|
|
G = the intersection of lines YP and ZX |
(5/7, 0, 2/7) - see below
|
Method 1: Ceva ratios
Method 2: Relations on line YP
(b) Suppose the plane of this triangle is projected to another plane, and point X is projected to X' = (2, 0, 0), Y is projected to point Y' = (1, 1, 1) and Z is projected to point Z' = (0, 0, -1). To what point W' is point W projected?
Since W = 1X + (-1)Y
+ 1Z, W' = 1X' + (-1)Y' + 1Z' = (1, -1, -2).
Problem 5
Let I = (1, 0, 0), J = (0, 1, 0), K = (0, 0, 1).
(a) In 3-space, let M be the midpoint of segment KI and let N be the midpoint of segment KJ. What are the 3-space coordinates of point M and point N?
M = (1/2)(K+I) = (1/2)(1, 0, 1) = (1/2, 0, 1/2)
N = (1/2)(K+J) = (1/2)(0, 1, 1) = (0, 1/2, 1/2)
(b) What is the (3-space) distance MN?
|MN| = sqrt of dot product (M-N) . (M - N)= sqrt ((1/4)+(1/4)) = (1/2)sqrt 2
Note: This is (1/2) |IJ|, which makes sense, since this is parallel to IJ and half as long by Thales.
Let S be the sphere of radius 1 with center O = (0, 0, 0). Points I, J and K are on this sphere.
(c) Let M' be the spherical midpoint of the spherical (great circle) segment KI. Let N' be the spherical midpoint of the spherical segment KJ. What are the 3-space coordinates of M' and N'?
M' = (1/|M|)M = (1/sqrt 2)(1, 0, 1)
N' = (1/|N|)N = (1/sqrt 2)(0, 1, 1)
(d) What is the spherical distance M'N'? (measured in degrees or radians)
If d is the spherical distance, d = angle M'ON' = angle MON.