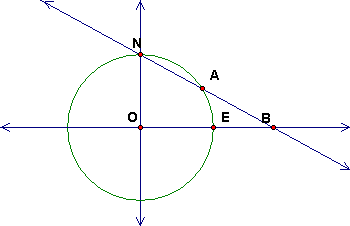
This cross-section shows stereographic projection from the sphere with center O of radius R, with center of projection at N to the equatorial plane perpendicular to the diameter ON.
The point B is the stereographic image of A, a point on the sphere.
Let c be a circle with radius R and center O. Suppose that the inversions of two general points A and B in c are A' and B'. Two (or more) of the triangles that can be formed from the points A, B, A', B' O are similar.
Write a pair of similar triangles.
Prove the similarity.
State briefly the key idea of how these similar triangles are used to prove that the inversion of a line not through O is a circle (with one point exception)
.
Suppose A, B, and C to be points on the real number line. If A = 1, B = 10, C = 46. For what point D does CD divide AB harmonically?
D = ____________
Define the radical axis of two circles c and d.
The radical axis of two circles is a line. Is this part of the definition or not? Yes ____ No _____
Given triangle ABC and points A' on BC, B' on CA and C' on AB. Suppose the ratio BA'/A'C = 4/3 and ratio CB'/B'A = 5/2.
(a) What are the barycentric coordinates (with respect to ABC) of P, the intersection of AA' and BB'?
Barycentric coordinates of P = __________________________
(b) If AA', BB' and CC' are concurrent, what is AC'/C'B?
AC'/C'B = ____________________________
(c) If A = (1, 1, 0), B = (0, 2, 1), C = (1, 1, 1) what point is P?
P = ______________________________________________
Let S be the sphere with center (0,0,0) and radius 1. The plane p with equation x+y+z = 1 intersects S in a circle c.
The circle c is a circle in the plane p, but it can also be considered as a spherical circle of points whose spherical distance from a center on the sphere is constant.
(a) What is the center C of this circle c in the plane p?
C = __________________
(b) What is the radius of c in plane p?
Radius = ________________________
(c) What is a center D of this circle on the sphere S?
D = __________________________
(d) What is a spherical radius of this circle? (angle measure or given as an inverse trig function)
Spherical radius = ___________________________________
(a) Given point K = (0,0,1) and point P = (a, b, c), write the parametric formula for line KP. Choose the parameter t so that t = 0 at K and t = 1 at P.
Parameterization: ___________________________________
(b) Use the parameterization above to write a formula in terms of (a, b, c) for the intersection Q of the line KP and the plane with equation z = 0.
Q = _______________________________
|
This cross-section shows stereographic projection from the sphere with center O of radius R, with center of projection at N to the equatorial plane perpendicular to the diameter ON. The point B is the stereographic image of A, a point on the sphere. |
|
· If A is 45 degrees from N in spherical distance, calculate the distance from O to B.
Distance (in terms of R) _____________
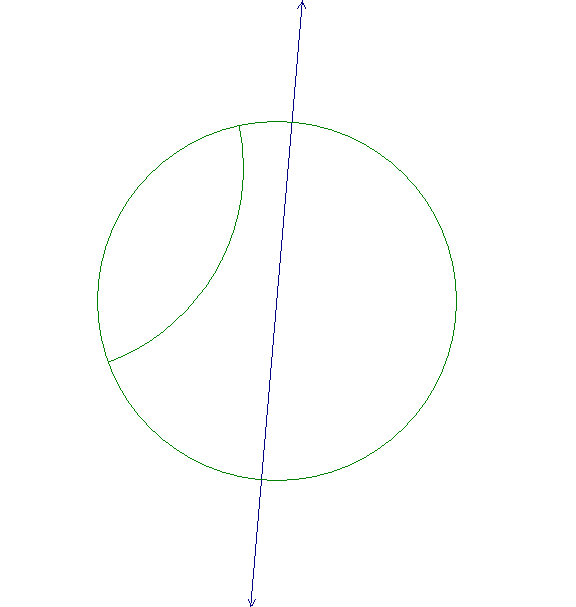
This figure shows two P-lines in the Poincaré disk model (one of the P-lines is a Euclidean segment). Construct the P-line m orthogonal to both of these lines.
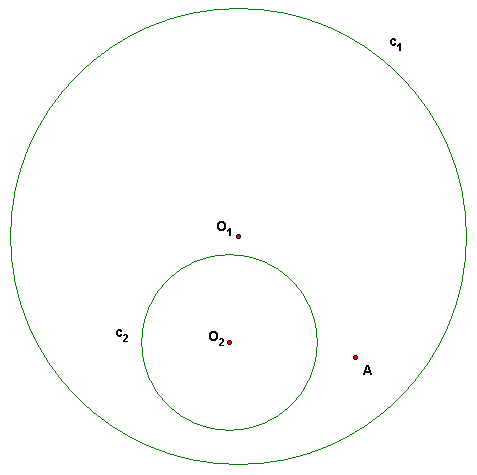
Write briefly and clearly your main steps. O1 and O2 are the centers of c1 and c2.
(a) Construct and label the circle m through A and orthogonal to c1 and c2.
(b) Construct and label the circle d through A that is in the same coaxal family (pencil) as c1 and c2.
(c) Construct and label a point N so that for a circle n with center N, the inversion images of c1 and c2 are concentric circles. (Just construct N. Do not invert!)
|
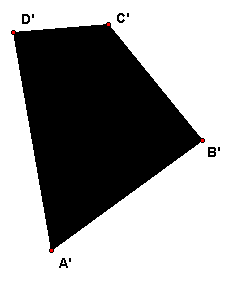
The figure on the right is made of 4 squares. The figure below shows a central projection (or perspective drawing) A'B'C'D' of the square ABCD. · Construct the rest of the projected figure. In other words construct points E', F', G', H', I' so that the new figure is a central projection of the one above to another plane. Write a few words, enough to make clear what you did. You do not need to justify your construction so long as it is clear. |
|
Do not write in this table. Reserved for Grader.
Problem |
Points |
Score |
|
1 |
25 |
|
|
2 |
15 |
|
|
3 |
15 |
|
|
4 |
25 |
|
|
5 |
25 |
|
|
6 |
20 |
|
|
7 |
15 |
|
|
8 |
15 |
|
|
9 |
25 |
|
|
10 |
20 |
|
|
Total |
200 |