Math 445 Winter 2003
The first couple of weeks we will be studying affine geometry. This name is
likely unfamiliar, but you will find that it is a kind of geometry that you
have seen before. The introduction to affine geometry will be the study of parallel
projection. The definition of affine geometry will be the geometry of relationships
in figures that still hold true when the figure is parallel-projected.
Class Discussion (for Assignment 1 see below)
Course info on web site:
http://www.math.washington.edu/~king/coursedir/m445w03/index.html
1. Review of basic properties of points, lines and planes
List the basic properties of points, lines and planes that do not involve angle
or distance.
- Two points determine
- Three points determine
- If two points of a line are in a plane, then the line …
- Two planes can be parallel or ….
- Three planes can meet ….
2. Parallel and skew lines in space
Definition: Two lines are skew lines if ________________
Definition: Two lines are parallel if ________________________
Theorem: If m is parallel to n and n is parallel to p, then m is parallel
to p.
- Write down a proof of this theorem. What facts about points, lines and
planes did you use?
- Give an example that shows this is not true if the word "parallel"
is replaced by "skew".
3. Parallel Projection Definition – State the definitions
- Definition: Parallel Projection of points in space to a plane ___
- Definition: Parallel projection of line plane to another. ___
- Special Case: Orthogonal Projection – see Berele Goldman ___
4. Projection of a line: What is preserved and what is changed?
- Why is the parallel projection of a line into a plane also a line? (Note
any special case exceptions.)
- Why is the midpoint of a segment projected to the midpoint of the image
segment?
5. Projection of Parallel lines
- Why is the projection of two parallel lines into a plane also a pair of
parallel lines? (Again note any exceptional cases.)
- In general, what kind of figure is the parallel projection of a square from
one plane into another?
Assignment #1 Due Wed 1/8
1-1
Group problem
You will be assigned to a small group. Your group will be assigned one of
the 5 topics/points above. The group should submit a Word Doc (or a text doc)
answering the questions, stating the definitions, completing the sentences,
etc.
1-2
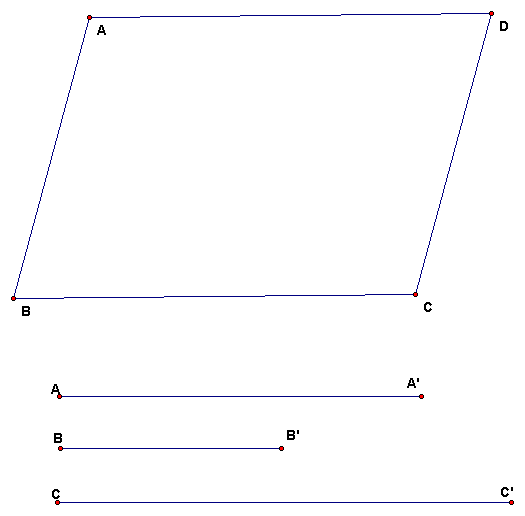
Make a model of a projection of a quadrilateral.
As we did in class for a triangle, make a slanted prism showing the orthogonal
projection of a quadrilateral ABCD "on the plane of the table" to
quadrilateral A'B'C'D' in another plane. You should figure out the length DD'
by reasoning, not just guessing. The model should be of cardboard or stiff paper.
- The bases ABCD should be the figure below (this size not smaller).
- The lengths of the segments AA', BB', CC' should be as shown.
- Tell how you figured out and constructed the length of DD'.