NAME __________________________________________________
Part A: Short Answer
Problem A1: Write True or False
a) A parallelogram is cyclic if and only if it is a rectangle. ___________
b) If lines AB and CD are parallel and segments BC and DA are congruent, then quadrilateral ABCD is an isosceles trapezoid. ___________
c) Every dihedral angle of a regular tetrahedron is 60 degrees. ___________
d) The circumcenter of a right triangle is the midpoint of the hypotenuse. ________
e) If S and T are isometries, then TS is the inverse of ST. ___________
Problem A2: Compositions of Isometries
Answer with one ore more names indicating all the possible kinds of isometry that are possible.
a) If S is a glide reflection and T is a line reflection, then ST can be a ______
b) If U is a translation and V is a glide reflection, then VU can be a _____________
c) Suppose point A is on line m. Then if M is line reflection in line m and N is point reflection in point A, MN can be a ______________
d) If E is a translation and F is a point reflection, EF can be a __________________
Problem A3: Complete these statements.
a) Definition: A symmetry of a figure F in the plane is ___________________ ________________________________________________________________
b) The angles at opposite vertices of a cyclic quadrilateral are __________________
c) The point of concurrence of the medians of a triangle is called the ____________
Problem A4: A Platonic Solid
Describe the regular dodecahedron, specifically:
(a) What is the shape of the faces? _____________________________
(b) How many faces meet at a vertex? ____________________
(c) How many faces are there in total? ___________________
(d) How many edges? ____________________
(e) How many vertices? ____________________
(f) What is the dual of the dodecahedron? ____________________________
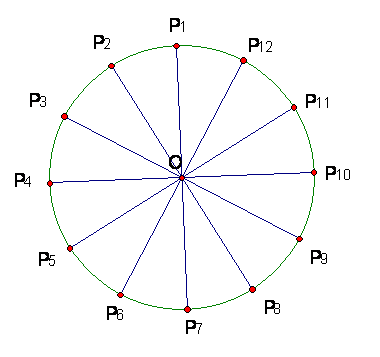
Problem A5In the circle, the center is O and the points on the circle are evenly spaced. · Denote by R1, R2, etc, the line reflections in OP1, OP2, etc. · Otherwise notation such as RP4P9 denotes line reflection in line P4P9. In your answers, specify
angles and rotation angles using degree measure and use given labels to give
centers, mirror lines, etc. whenever possible. |
|
(a) How many line reflections are symmetries of this figure? _________
(b) How many rotations are symmetries of this figure? _________
(c) Give the measure of angle P1OP2. _________
(d) Give the measure of angle P3P2P8. _________
(e) Tell what isometry is R1R2:___________________________________
(f) Tell what isometry is R1R5R2:___________________________________
(g) Tell what isometry is RP9P7 RP3P7:___________________________________
(h) If Q is the intersection of the lines P11P9 and P5P8, give the measure of angle P11QP5. _________
(i) Tell what isometry is R 1 R P7P5 RP5P1 _______________________________
Part B.
ANSWER 2 of the 3 problems in Part B
Show briefly the steps in your reasoning.
Problem B1
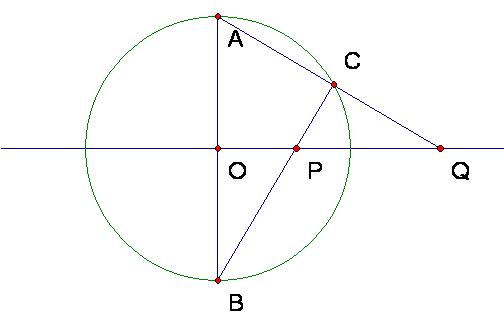
In the figure, O is the center of a circle of radius R, and OP is perpendicular to AB.
If OP = d,, find OQ in terms of R and d, if possible.
Show briefly the steps in your reasoning.
Problem B2: Some Ratios
In this figure of triangle ABC, point D is on AB and point E is on AC. Then F is the intersection of CD with BE, and G and H are the intersections of line AF with DE and BC, respectively.
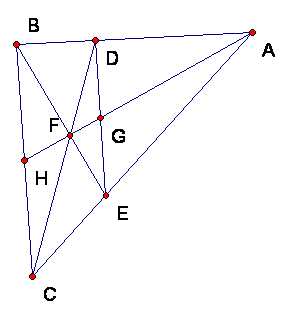
If in addition, we are given that AD/AB = 2/3 = AE/AC, compute the ratios below.
Use the bottom of the page as needed for your work, but write your answer in the spaces indicated.
a) Ratio AG/AH = ________________
b) Ratio FG/FH = __________________
c) Ratio HF/HA = _________________
d) Area FBC/area ABC = ________________
Problem B3: Two rays
Given point D on ray AB and point E on ray AC, suppose that the distances between points are |AB| = c, |AC| = b, and also |AD| = 7/b and |AE| = 7/c.
Show your reasoning briefly below but write the answers in the indicated spaces.
a) If BC = a, what is the length of DE? _____________________
b) Is line BC parallel to line DE? ____________________
Part C: Answer both C1 and C2
Problem C1
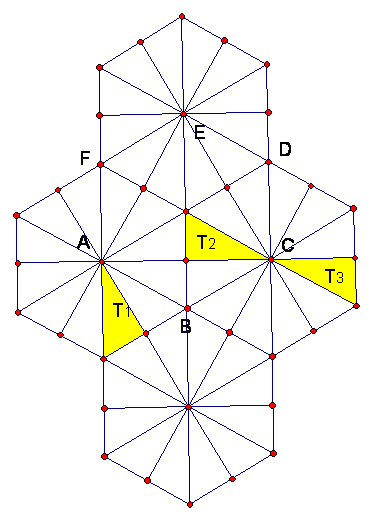
|
a) What isometry F will map triangle T1 to triangle T2? Write defining data and name. ____________________ b) Find a product of line reflections M1 or M2M1 or M3M2M1 equal to F. Label the lines in the figure as m1, m2, m3 (as many as needed). c) What isometry G will map triangle T2 to triangle T3? Write defining data and name. ____________________ d) Find a product of line reflections N1 or N2N1 or N3N2N1 equal to G. Label the lines in the figure as n1, n2, n3 (as many as needed). e) Tell what isometry is GF and give its defining data. ____________________ |
|
Problem C2: Pyramid
Show your work below but write your answers in the indicated spaces.
Consider a pyramid ABCP with base an equilateral triangle ABC and vertex P directly above the center O of ABC.
Suppose the side lengths of ABC = s and also the height of the pyramid = s.
(a) Calculate the exact dihedral angle between triangle ABP and triangle ABC (you can leave the angle in the form of the inverse trig function of an angle measure).
Dihedral angle = _____________________
(b) Calculate the volume of this pyramid.
Volume = _____________________
Part D
Prove ONE of the following theorems.
I. The medians of a triangle are concurrent.
II. If ABC is congruent to DEF, there is an isometry T that is the composition of 1, 2 or 3 line reflections such that T(A) = D, T(B) = E, T(C) = F.
III. If ABCD is a trapezoid with parallel sides AB and CD, the line MN through the midpoint M of AB and the midpoint N of CD passes through the intersection point P of the diagonals AC and BD.