Definition of Line Reflection:
Your Definition: ________________________________________________
Let m be a line and S be some figure. If the reflection S' of S in line m is the same as S, then we say that S has line symmetry with line of symmetry m.
Triangles with a Line of Symmetry
Conjecture: If the triangle ABC has a line of symmetry, what kind of triangle is ABC? How is the line related to ABC?
WriteYour Conjecture: _______________________ …
Conjecture: If the triangle ABC has two lines of symmetry, what kind of triangle is ABC? How are the lines related to ABC?
WriteYour Conjecture: _______________________ …
If you wanted to prove your conjecture, you could try the following approach. Consider several possible cases.
Answer:
Quadrilaterals with a Line of Symmetry
Circles, Equilateral triangles, rectangles
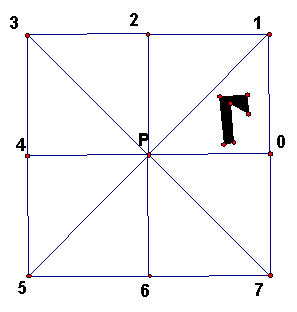
Start with the center P and point 0. Construct a square as in the figure, divided into 8 congruent right triangles as in this figure. Number the endpoints of the segments as shown. Then draw freehand a"blob" (it is a general polygon interior) and place it as shown.
Goal: To understand the effect of multiple reflections and see how multiple reflections explain the view into a kaleidoscope.

Important: Use File > Document Options to make a 4 additional pages in your GSP document that are each a copy of your first page with the square above. You will need it later.
We will be studying the effects of reflecting the blob, which we call S. Here is the notation we will use.
If n is a number, Rn means reflection in line Pn. For example R0 is reflection in line P0, R1 is reflection in line P1, etc.
Composition: For any object T, RjRi(T) means FIRST reflect by Ri and SECOND reflect by Rj.
Experiment 1. One the first page, fill in a pattern by reflecting S and its images by various Ri to get as many blobs as possible. What are the lines of symmetry of the result?
Experiment 2. Start afresh with your copy on page 2. Fill in the pattern by reflecting S and the images of S (and their images, etc.) but this time only use R1 and R0 over and over in any order you want.
Experiment 3. Start afresh with your copy on page 3. Fill in the pattern by reflecting S and its images only using R2 and R3 over and over in any order you want.
Experiment 4. Start afresh with your copy on page 4. Fill in the pattern by reflecting S and its images only using R2 and R0 over and over in any order you want.
If one takes two hinged mirrors that meet at an angle of 45 degrees, the kaleidoscopic pattern always has 8 congruent parts and 4 lines of symmetry.
If one takes two hinged mirrors that meet at an angle of 90 degrees, the kaleidoscopic pattern always has 4 congruent parts and 2 lines of symmetry.
Experiment 5. In any of your sketches, draw a new point Q in the plane and reflect by R0 to get Q' and reflect Q' by R1 to get Q''.
Experiment 6. Start afresh in a blank sketch, and draw two lines PA and PB. Repeat experiment 5 with reflections in these lines. (Specifically, Q' = reflection of Q in PA and Q'' = reflection of Q' in PB.) Measure the angles with Sketchpad. Look for the relation between angle APB and angle QPQ''.
Big Questions