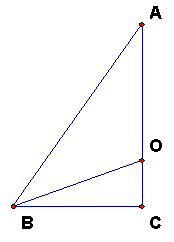
Triangle ABC is a right triangle with AB = sqrt 3, CA = sqrt 2, BC = 1.
Let O be a point on AC so that for some R, AO = OB = R.
a) Find R using the Pythagorean theorem for BCO.
b) Also, compute AO/AC.
Read:
Problems related to Cube and Tetrahedron: Lengths from similar triangles
|
Triangle ABC is a right triangle with AB = sqrt 3, CA = sqrt 2, BC = 1. Let O be a point on AC so that for some R, AO = OB = R. a) Find R using the Pythagorean theorem for BCO. b) Also, compute AO/AC. |
|
|
In this figure, the triangle ABC is isosceles, with AB = AC = s, AN = h, and BN = g, where N is the midpoint of BC. Line MO is the perpendicular bisector of AB. a) Show the right triangle ABN is similar to the triangle AOM. b) What is the scaling factor K from ABN to AOM? (If one multiplies the side lengths of ABN by K one obtains the corresponding side lengths in AOM.) c) Use your K to find the ratio AO/AN in terms of s, h, g. d) Finally, suppose that s = sqrt 3, h = sqrt 2 and g = 1. Check that your answer for AO/AN is the same as the ratio computed in Problem 1. |
|
Use one of the problems above and your earlier work on altitudes of regular tetrahedra to find the radius of the circumsphere about the regular tetrahedron.
Compute a dihedral angle of a regular tetrahedron. (All the angles are the same.)
Compute all the dihedral angles of a pyramid with a square base and 4 equilateral triangles as faces. (How many different angles are there?)
Read Brown and answer the following questions:
Prove that reflection in a point O is an isometry.
If T is an isometry and A'B'C' is the image of triangle ABC by mapping T, explain why A'B'C' is congruent to ABC.
Prove that the composition of two isometries is an isometry.