Do all problems. Total points = 50 points.
In any of the questions if you are asked to construct the defining data of an isometry, this means to construct what you would need to define the isometry (in theory or in Sketchpad). For a line reflection, this means construct the mirror line. For a rotation, construct the center and angle. For a translation, construct the translation vector AB, for a glide reflection, construct the invariant line m and the glide vector AB.
(a) Define isometry of the plane.
(b) Explain (informally but convincingly) why isometries preserve angle measure, even though nothing about angle is in the definition.
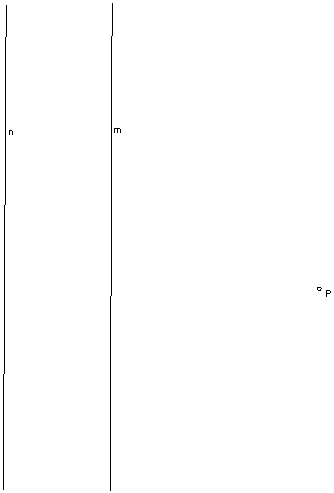
Let M and N be the reflections in parallel lines m and n in the figure. Point P is the point shown. With straightedge and compass, construct the point Q = MN(P). (Hint: This may seem a bit tricky, but think twice before jumping to conclusions.)

Given the line AB below, let M be reflection in line AB and let R be rotation by 45 degrees (counterclockwise as always) with center A.
(a) Tell in words precisely what isometry is the isometry T = MR.
(b) In the figure below, construct the defining data for T.
![]()
Suppose that each of E, F, G, H, J and K are glide reflections. Let U = EFGHJK.
It may be impossible to say precisely what kind of isometry U is, but it may be possible to narrow down the possibilities. Circle the names of isometries below that U could possibly be. Then in a sentence or two, give a reason for your answer. (This is an informal answer, just be convincing but not lengthy.)
(a) Identity
(b) Line Reflection
(c) Point Reflection
(d) Translation
(e) Rotation
(f) Glide Reflection
Reason:
In the (x, y) plane, let F(x, y) = (x + 2, y – 6). Write the equations of two lines, m and n, so that if M and N are the reflections in these lines, F = MN.